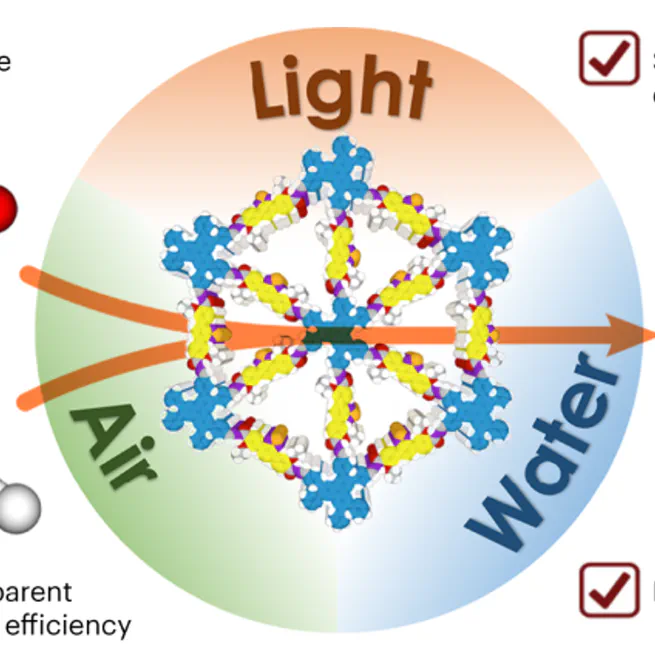
Abstract Charge transfer and mass transport to catalytic sites are critical factors in photocatalysis. However, achieving both simultaneously is challenging due to inherent trade-offs and interdependencies. Here we develop a microporous covalent organic framework featuring dense donor–acceptor lattices with engineered linkages. The donor–acceptor columnar π-arrays function as charge supply chains and as abundant water oxidation and oxygen reduction centres, while the one-dimensional microporous channels lined with rationally integrated oxygen atoms function as aligned conduits for instant water and oxygen delivery to the catalytic sites. This porous catalyst promotes photosynthesis with water and air to produce H2O2, combining a high production rate, efficiency and turnover frequency. This framework operates under visible light without the need of metal co-catalysts and sacrificial reagents, exhibits an apparent quantum efficiency of 17.5% at 420 nm in batch reactors and enables continuous, stable and clean H2O2 production in flow reactors.
Feb 13, 2024
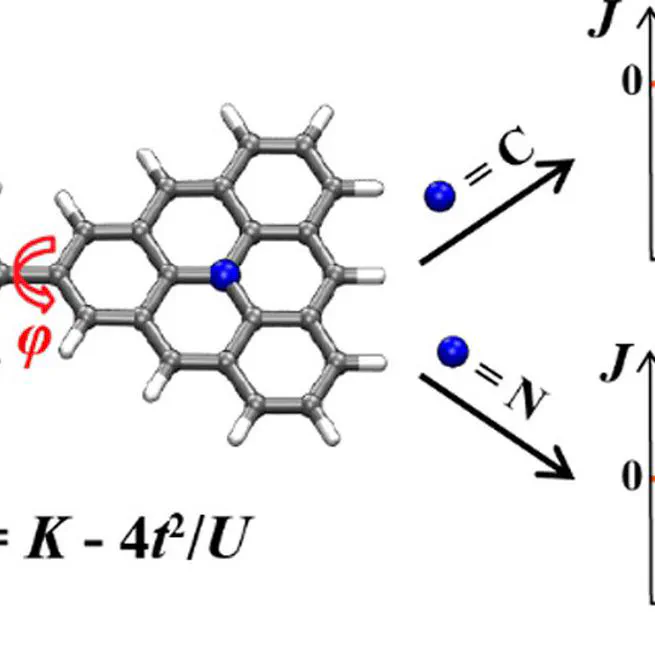
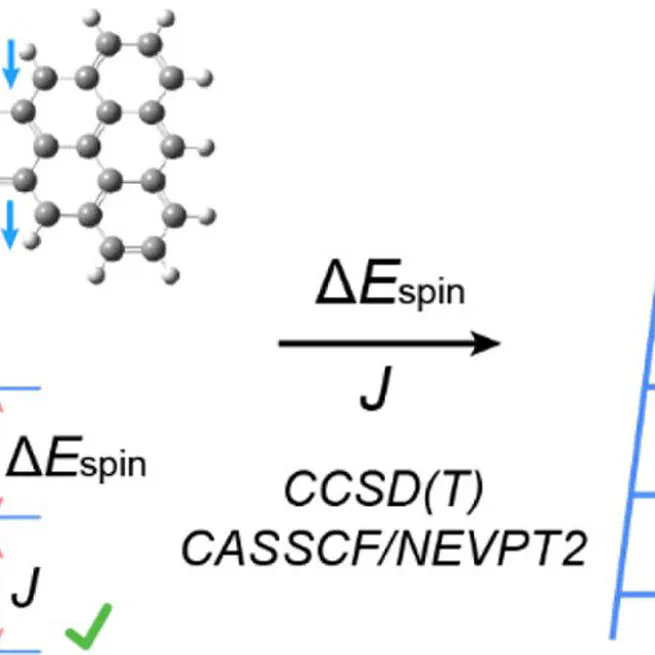
We present an effective approach to control the magnetic couplings in triangulene dimers. We investigated 24 triangulene dimers and achieved unprecedented strong J values up to -144 meV. Many of our predictions have been experimentally verified. We show the first example of ferromagnetic triangulene dimers that is beyond Lieb's theorem's predictive power.
Aug 23, 2023
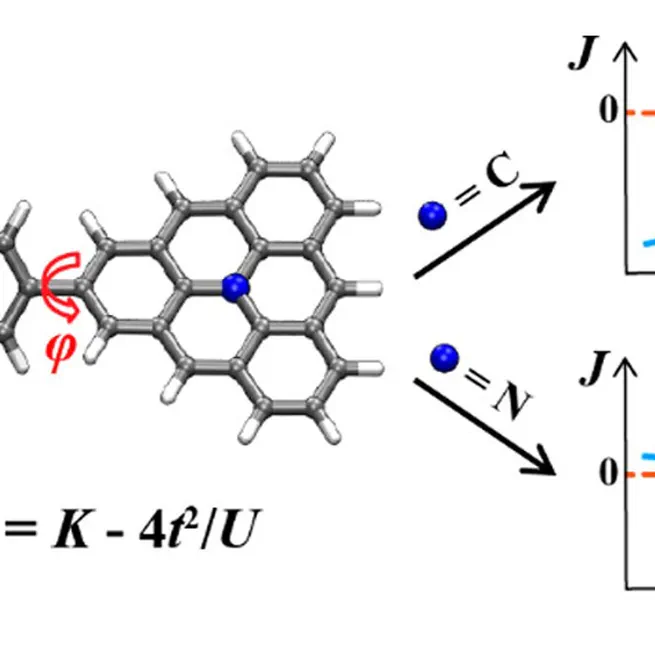
We present an effective approach to control the magnetic couplings in triangulene dimers. We investigated 24 triangulene dimers and achieved unprecedented strong J values up to -144 meV. Many of our predictions have been experimentally verified. We show the first example of ferromagnetic triangulene dimers that is beyond Lieb's theorem's predictive power.
Aug 23, 2023
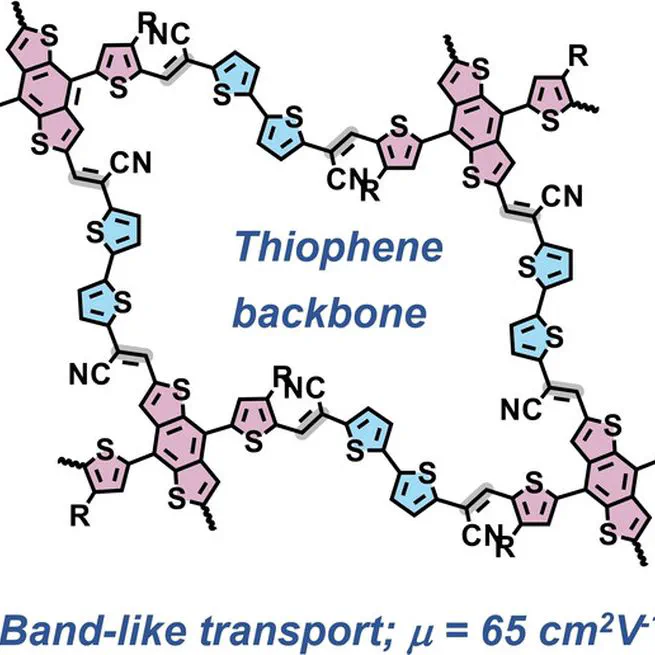
Abstract Linear conjugated polymers have attracted significant attention in organic electronics in recent decades. However, despite intrachain π-delocalization, interchain hopping is their transport bottleneck. In contrast, two-dimensional (2D) conjugated polymers, as represented by 2D π-conjugated covalent organic frameworks (2D c-COFs), can provide multiple conjugated strands to enhance the delocalization of charge carriers in space. Herein, we demonstrate the first example of thiophene-based 2D poly(arylene vinylene)s (PAVs, 2DPAV-BDT-BT and 2DPAV-BDT-BP, BDT=benzodithiophene, BT=bithiophene, BP=biphenyl) via Knoevenagel polycondensation. Compared with 2DPAV-BDT-BP, the fully thiophene-based 2DPAV-BDT-BT exhibits enhanced planarity and π-delocalization with a small band gap (1.62 eV) and large electronic band dispersion, as revealed by the optical absorption and density functional calculations. Remarkably, temperature-dependent terahertz spectroscopy discloses a unique band-like transport and outstanding room-temperature charge mobility for 2DPAV-BDT-BT (65 cm2 V−1 s−1), which far exceeds that of the linear PAVs, 2DPAV-BDT-BP, and the reported 2D c-COFs in the powder form. This work highlights the great potential of thiophene-based 2D PAVs as candidates for high-performance opto-electronics.
Jun 4, 2023
We developed a benchmark dataset comprising 25 magnetic systems with nonlocal spin densities, including triangulene monomers, dimers, and their analogues. This work highlighted the importance of the choice of DFT functional.
Jun 1, 2023
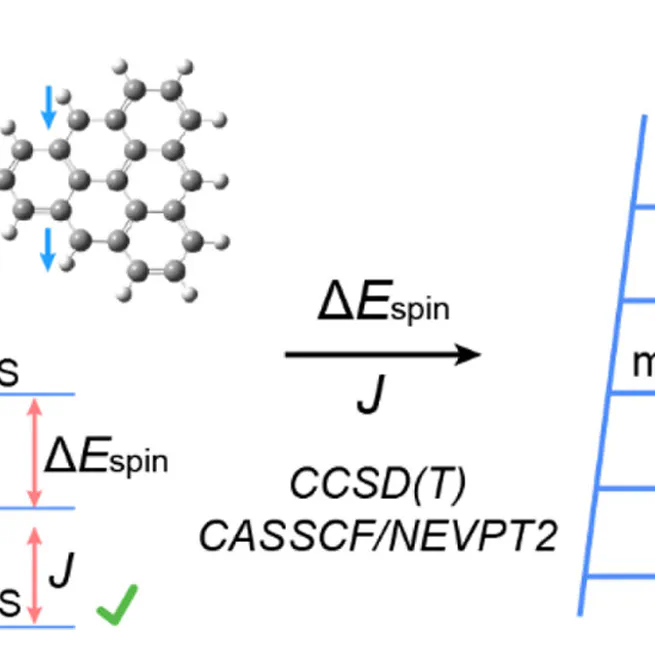
We developed a benchmark dataset comprising 25 magnetic systems with nonlocal spin densities, including triangulene monomers, dimers, and their analogues. This work highlighted the importance of the choice of DFT functional.
Jun 1, 2023
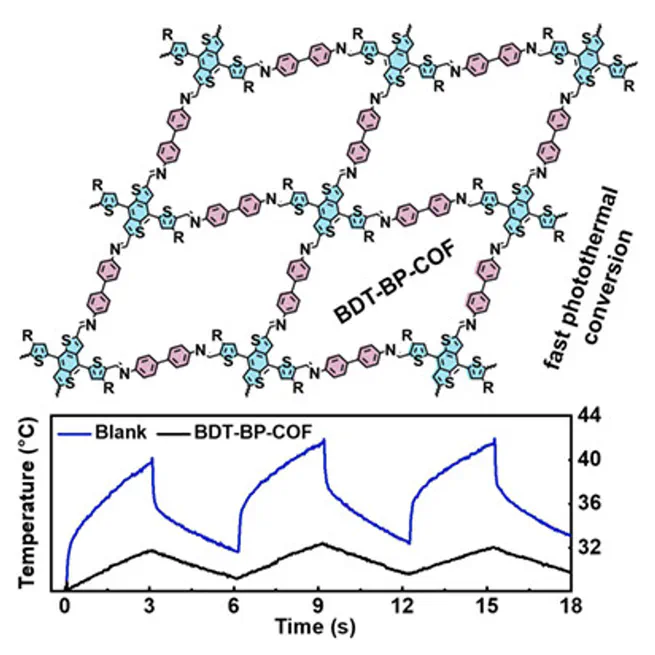
Abstract Two-dimensional conjugated covalent organic frameworks (2D c-COFs) are emerging semiconductor materials for optoelectronic and photothermal applications. In particular, the highly tailorable, semiconducting thiophene-based 2D c-COFs have attracted considerable interest due to their nontrivial physicochemical properties such as photo-activity, broad optical absorption, tunable electronic structures, and so forth. Herein, we demonstrate a novel, crystalline 2D c-COF based on thienyl-functionalized benzodithiophene (BDT) and biphenyl (BP) via the Schiff-base polycondensation reaction. The resultant BDT-BP-COF exhibits a broad optical absorption up to ca. 600 nm and decent π-conjugation along the 2D polymer skeleton, as revealed by the optical absorption and theoretical calculations. The favorable π-conjugation and the abundant electron-rich thiophene units confer excellent photo-activity to BDT-BP-COF towards the usage of solar energy. As a proof-of-concept application, we explore BDT-BP-COF in photothermal conversion, in which it shows a fast surface-temperature increase upon light irradiation for seconds.
Apr 7, 2023
Jun 22, 2022
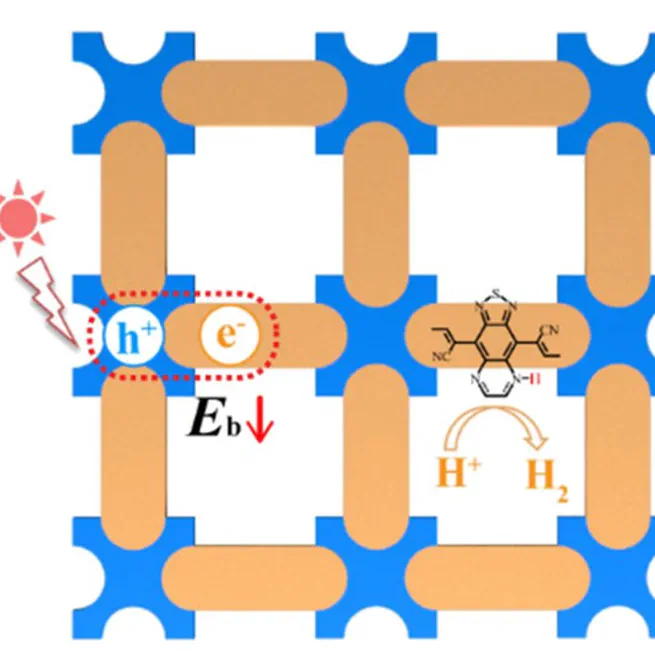
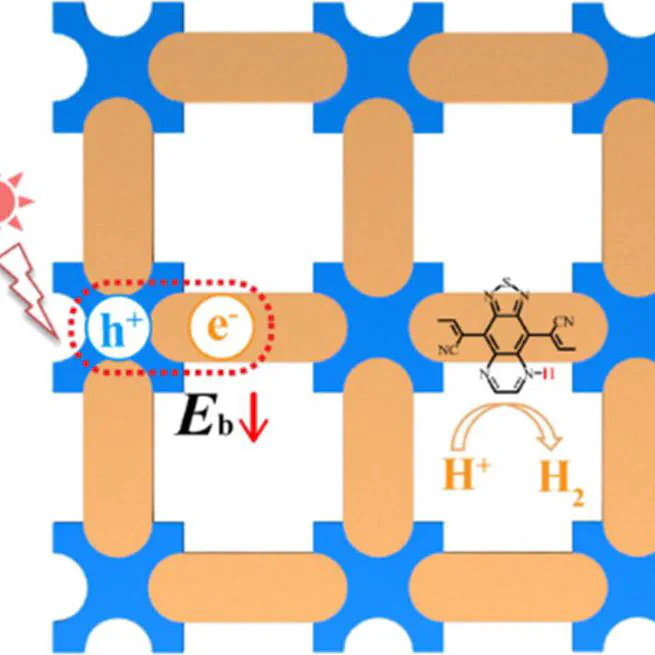
Abstract Photocatalytic hydrogen generation is a promising solution for renewable energy production and plays a role in achieving carbon neutrality. Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) with highly designable backbones and inherent pores have emerged as novel photocatalysts, yet the strong excitonic effect in COFs can impede the promotion of energy conversion efficiency. Here, we propose a facile approach to suppress the excitonic effect in COFs, which is by narrowing the band gap and increasing the dielectric screening via a rational backbone design and chemical modifications. Based on the GW-BSE method, we uncover a linear relationship between the electronic dielectric constant and the inverse square of the optical band gap of COFs of the Lieb lattice. We further demonstrate that both reduced exciton binding energy and enhanced sunlight absorption can be simultaneously realized in COFs with a narrow band gap. Specifically, we show that one of our designed COFs whose exciton binding energy is nearly half that of g-C3N4 is capable of metal-free hydrogen production under near-infrared light irradiation. Our results showcase an effective method to suppress the excitonic effect in COFs and also pave the way for their applications in photocatalytic, photovoltaic, and other related solar energy conversions.
Jun 22, 2022
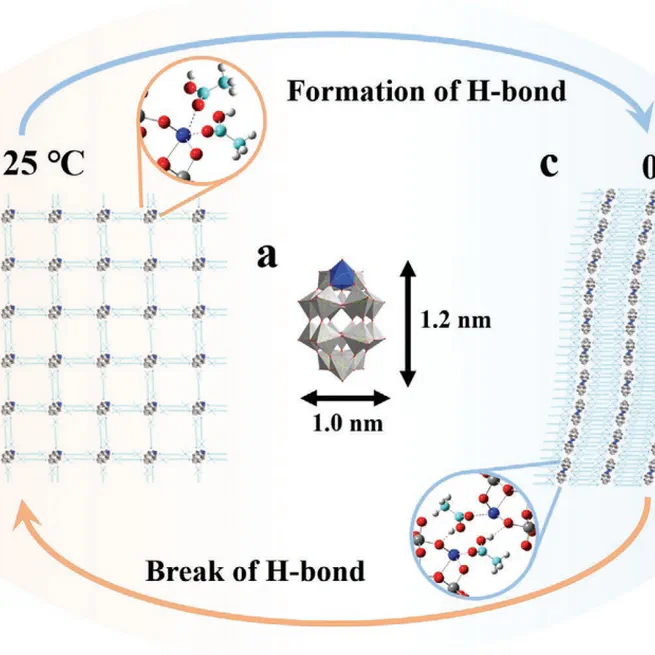
Abstract Smart materials that can respond to external stimuli are typically prepared through the coating of specific responsive ligands. Herein, for the first time, thermally reconfigurable single polyoxometalate (POM) cluster assemblies without temperature-responsive surfactants are reported. Based on transmission electron microscopy observation, POM clusters are obtained to arrange into a 2D single cluster superlattice at 25 °C, and transform themselves into a single cluster nanowire below 0 °C, which is caused by the switching of hydrogen bond linkage between clusters. Contributed by the specific coordinative state, the POM assembly exhibits excellent catalytic activity and stability toward olefin epoxidation at room temperature, demonstrating the application potentials of the nanostructures based on single clusters.
May 20, 2021